
I leave work every day at five o’clock.ģ.

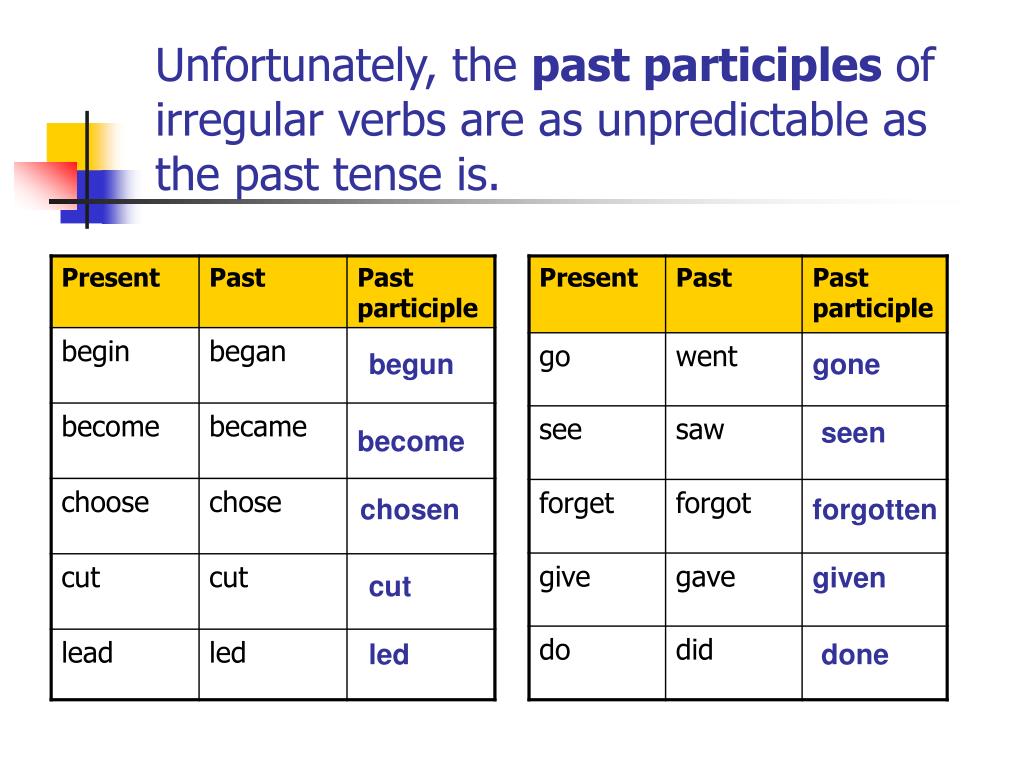
These verbs have the same form in both past simple and past participle, but the base form of the verb is spelled and pronounced differently. Below are some examples: Base VerbĬategory Two: Verbs that have a different base form but the same past simple and past participle forms. These verbs are spelled the same and sound the same in each form. When we want to show that something has happened in the past, either past simple or past participle, an irregular verb will essentially fall into one of four main categories.Īgain, do not feel that you need to memorize each of these categories, but they will help you to recognize patterns as you become more familiar with spelling changes and verb nuances.Ĭategory One: Verbs that have the same base form, past simple, and past participle forms. Image by David Travis via Unsplash Four Categories of Irregular Verbs in Past Tense You can see that the helping verb (had) is added before the irregular verb “eaten.” Because the verb phrase “had eaten” refers to something that has been completed prior to another event (leaving for work), it is a past participle verb form. Here is an example: Yesterday, I had eaten yogurt for breakfast before I left for work. Past participles are a little bit different in that they are usually combined with a helping verb and show that some action has been completed before another event or prior to the present. Similarly, in sentence number two, the base form of the verb is “go,” while the simple past form is “went.” In these cases, the word changes entirely rather than adding an -ed suffix. In sentence number one, the base verb is “eat,” and the simple past form is “ate.” The verbs above are irregular because the base verb form is different from its past tense form. Simple past refers to something that has happened in the past and has been completed independent of other events ( source).ġ. Both the simple past and past participle forms are often spelled differently.ĭon’t get too caught up in the differences between simple past and past participles, but you should understand the nuances in each. Irregular verbs do not follow the normal patterns and rules, and you cannot change an irregular verb from present to past tense by adding -ed ( source). There are about 200 or so in the English language, and while you certainly do not need to memorize them, as you become more familiar, it’ll become easier to spot them. Irregular verbs, however, are not as simple. However, when regular verbs end in a consonant followed by a “y,” the base form of the verb will also change in spelling, like these: Base Verbīase verbs that end in a consonant followed by a “y” require you to change the “y” to an “i” before adding your -ed suffix. Below are a few examples of base verbs that are regular. Regular verbs are the easiest to change from present tense to past tense - you simply need to add the suffix -ed to the base form of the verb. In addition to there being three categories or types of verbs, each performing a specific function in your sentence, there are also both regular and irregular verbs.

Read more to learn about the differences between regular and irregular verbs and how they are changed from present to past tense.
For irregular verbs like “run,” the spelling of the word changes entirely.

While many regular verbs can be changed from present to past tense simply by adding the suffix “ed,” the verb “run” is different. The past tense of “run” is “ran.” In the English language, verbs can be either regular or irregular. It can be tricky, though, to remember how to do so correctly with irregular verbs. It’s important to distinguish between past and present tense in your writing so that your reader understands what is happening now versus what happened days, months, or moments before.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
